The last class before the winter holidays we were just about to start with the "sliding theory" for the explanation of muscle movement.
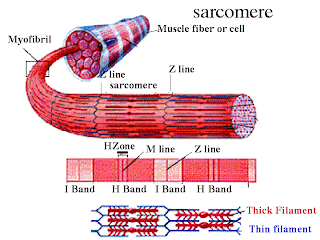
A sarcomere is a unit within the muscle responsible for the movement, the muscle fibre is a continuity of repetitive units or sarcomeres.
Under the microscope the skeletal muscle fibre looks striated. Each fibre is built up by thick and thin filaments. The first one is the MYOSIN protein and the second one the ACTIN protein. Here you have a scheme representing the conformation of skeletal muscle with the dark or thick filaments and the light or thin filaments. A band: include part of thin filaments and the entire thick ones. I bands are only thin filaments. One sarcomere goes from one Z line to the next one.
The diagram below describe the arrangements of actin and myosin. Please note that actin filaments are made of chains of globular actin molecules. Myosin chains instead have characteristic globular heads and long tails.
There are two regulatory proteins: tropomyosin and troponin. They are on the actin filaments. Imagine that each actin filament is built up by a sequence of spheres with holes or actin sites.
At rest, when there is no contraction these sites are covered by tropomyosin molecules. The condition of no contraction happens when the level of calcium is low.
When the level of calcium increased, calcium binds to troponin molecule. These new complex makes the tropomyosin to free the actin sites. Now the actin sites can be occupied by myosin heads (cross bridges).
During contraction, myosin heads in the thick filaments bind to the actin sites in the thin filaments and pull them towards the middle of the sarcomere. This attachments between myosin and actin is regulated by the two named regulatory proteins.

The end result is a shortening of the sarcomere.
| The distance between the Z discs shortens | |
| The H zone disappears | |
| The dark A band increases because the actin & the myosin overlap more | |
| The light I band shortens. |
 |
In this upper figure it can be seen the arrival of the action potential, the releasin of neurotransmitter (acetylcholine) and the releasing of calcium within the skeletal muscle causing contraction! (you have to know this!!!).
In the figure below a flow diagram of contraction/relaxation (SLIDING FILAMENT THEORY) can be seen: